You may have seen ads touting peptides in skin care products and various supplements and found yourself wondering: What are peptides, anyway? Are they worth your attention, and could they make a difference in your health?
Yes, peptides are definitely worth your attention. Keep reading to learn more about the science behind peptides and how they could help you reduce overall inflammation, slow down the aging process, and benefit your health in several ways.
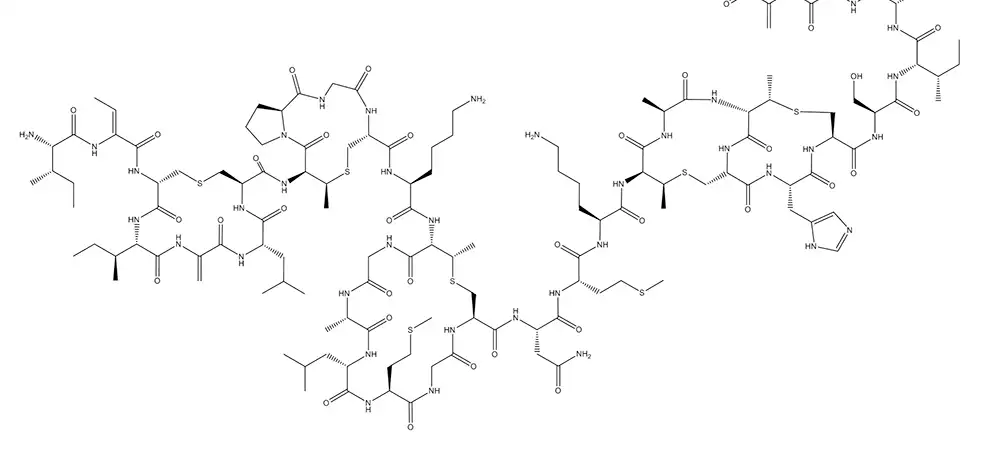
What Are Peptides?
Peptides are strings of amino acids similar to proteins, which are also made up of amino acids. Because peptides are very small, sometimes consisting of only two amino acids, they’re typically easy for the body to absorb, whether through the gut or the skin.
Your body makes peptides as part of its normal function; these are known as endogenous peptides. Insulin, for instance, is an endogenous peptide that consists of 51 amino acids.
In addition, peptides are present in foods, including meats, soy, milk, oats, wheat, and eggs. These are known as exogenous peptides. Scientists can also synthesize peptides in the lab. Insulin is also an excellent example of this process as the first peptide ever created in a lab.
Different types of peptides have different effects within your body, depending largely on what types of amino acids they contain. They’re instrumental in all sorts of your body’s processes, ranging from digestion to healing to communication between cells.
Exogenous peptides typically have fewer side effects than various medications because they’re natural to your body and because your body breaks them down into natural amino acids. They also travel easily throughout your body, making them easy to process.
Peptides vs. Proteins
When you hear the phrase “amino acids,” you probably think immediately of proteins — and you’re correct. Proteins are also chains of amino acids. So what’s the difference between proteins and peptides?
The difference lies in the size of the chain of amino acids involved. Shorter chains of amino acids are labeled peptides, while longer chains are called proteins. Most scientists will call a chain of 20 or fewer amino acids a peptide.
The short length of peptides is what enables these substances to work their way easily through the walls of skin, cells, and the intestines. That means they can get into the bloodstream and travel to the parts of the body where needed quickly and easily. For scientists making exogenous peptides, this property is a bonus, as the shorter length of peptides also makes them easier to create and produce.
Types of Peptides
Scientists classify peptides based on their properties and functions. Among the most common peptides are:
- Anticancer peptides: These small peptides fight cancer cells by breaking holes in cancer cell membranes; scientists use them in cancer treatment.
- Antifungal peptides: These peptides protect you against disease and infection stemming from fungi, including molds.
- Antimicrobial peptides: These endogenous peptides play a role in your immune response and help defend your body against intrusive and dangerous organisms.
- Bacterial peptides: These are produced by the bacteria in your body and include lipoproteins and some enzymes.
- Cardiovascular peptides: These help control your blood pressure and help fight congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, and atherosclerosis.
- Endocrine peptides: These specialized peptides help your endocrine system function properly through improving insulin sensitivity, boosting metabolism, regulating appetite and weight, fighting inflammation, regulating bone growth, and managing the sleep/wakefulness cycle. They also help control thyroid and sex hormones.
- Neuropeptides: Your neurons create these peptides, which work within your nervous system and brain; they include familiar body chemicals such as epinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine.
- Opiate peptides: These work with your hypothalamus and pituitary gland to mediate stress and pain.
- Plant peptides: These exogenous peptides, which you ingest from plants, help regulate cholesterol and blood pressure, and they also protect against inflammation, cancer, microbes, and damage caused by free radicals.
Scientists synthesize various types of peptides to boost health in a variety of ways. Synthesized creatine peptides, for instance, help build muscle strength, while synthetic collagen peptides show great benefits for skin health.
How Can Peptides Benefit Your Health?
Peptides, whether produced naturally in your body or synthesized in a lab, can benefit your health in a myriad of ways.
Improved Healing
Peptides play a role in healing in many ways. Collagen is one of the peptides that promotes healing. It’s active both in wound healing and in maintaining healthy skin. Certain antimicrobial peptides also may contribute to healing of certain skin conditions, including eczema and psoriasis. Varied bioactive peptides also behave as antioxidants, boosting healing as they decrease inflammation.
Slowing of the Aging Process
Various peptides help slow aspects of aging in different ways. Peptides delivered to the skin may protect against damage from the sun and increase blood flow to the skin. As a result, they can help boost skin elasticity and minimize the development of wrinkles. Inside your body as well, these peptides, which often include collagen, help your muscles, ligaments, and tendons stay flexible and strong, so you feel younger from the inside out.
Prevention of Bone Loss
Studies show that peptide intake may help counteract bone loss, which most people are likely to experience as they grow older. Peptides appear to increase bone mineral density, and some peptide-based medications have been approved as a treatment for osteoporosis.
Building of Muscle Mass
Certain peptides, including human growth hormone peptides, successfully help increase muscle mass, especially when paired with resistance training. They also assist with repair of damaged muscles and improve joint mobility. Of course, that doesn’t mean that all supplements that claim to build muscles are safe for you to take over the counter. Some supplements that contain peptides (or claim to contain them) have dangerous side effects, including raising blood sugar levels. That’s why it’s important to work with medical professionals when considering peptide use.
Improved Skin and Hair
Some of the antimicrobial peptides that your body makes naturally help your skin stay healthy, protecting your skin against damage from wounds and bacteria. Adding exogenous versions of these peptides can protect you against eczema, psoriasis, and acne. Typically, these exogenous peptides contain collagen, which is well-known for its ability to boost skin’s elasticity and moisture levels, as well as for helping hair become thicker and healthier. Also well-known is the fact that we lose collagen naturally with age — so peptide treatment may be necessary to protect your skin and hair as you grow older.
Increased Testosterone Levels
Specific peptides trigger the production and release of the hormones involved in the production of testosterone. By taking in these peptides, you can boost your body’s testosterone levels naturally without having to take supplemental testosterone.
Benefits to Brain Function
Among the benefits of opiate peptides is the ability to ease anxiety, depression, and stress, as well as to provide pain relief. Research is ongoing to determine how exogenous versions of these peptides, which bind with specific receptors in the brain, might help improve brain function and reduce stress medically.
Peptide Therapy
With peptide therapy, medical professionals can use peptides to improve your body’s function, with benefits to your bones, muscles, skin, brain, and other organs. Peptide therapy is delivered in a variety of fashions, depending on the peptides involved and the desired effect. Some peptides are delivered as injectables, while others are designed to be absorbed through the skin, either through topical application or transdermal patches. Peptide treatment is also available, in some cases, as oral or dietary supplements and even as nasal sprays. More than 80 types of peptide-based medications have been approved, which treat everything from diabetes and osteoporosis to HIV and testosterone deficiency.
Side Effects of Peptide Use
Because peptides are naturally occurring substances in the human body, side effects tend to be minimal. Even exogenous peptides, such as those occurring in food, typically have no side effects. In some cases, exogenous peptides are broken down into individual amino acids before they enter the bloodstream.
People who are pregnant or breastfeeding shouldn’t seek out peptide therapy without consulting first with their doctor. In some cases, peptides may be inappropriate for people taking specific medications or living with certain chronic conditions. Again, consultation with a doctor is a good idea before embarking on any type of medical therapy, including peptide therapy.
Though side effects are rare, some people may experience an allergic reaction to some peptides, resulting in hives, swelling, heart palpitations, difficulty breathing, nausea, diarrhea, headaches, or dizziness. In some cases, individuals with skin sensitivities may react to topical creams that contain peptides with itching or rashes. In the event of any such side effects, consult the doctor who prescribed the peptides.
The Future of Peptides
Research into the medical use of peptides is growing with leaps and bounds. As new formulations of peptides prove their efficacy at slowing down the aging process, building muscle, and protecting the body against various types of damage, you shouldn’t be surprised to learn of new uses for these useful chains of amino acids in the near future.
However, much of the ongoing research is cutting-edge. That means it’s important to work with medical professionals when seeking to harness the advantages and benefits of peptide therapy for your own body’s health. Your doctor is best positioned to discuss the potential benefits, the appropriateness of specific peptide therapy for your own situation, and any potential risks. Taking random supplements bought over the counter or off the internet is never wise, especially when you’re trying out fairly new medical therapies.
What Could Peptides Mean for You?
More peptides are being tested on an ongoing basis to find new ways to exploit these valuable medications. Over the last 30 years, the research on peptides has increased by more than 1,300%, with more on the way.
We’re dedicated to staying up to date on all the cutting-edge research being done on peptides. That’s because we want to help you seek and achieve the best health you can experience. Whether it’s the amazing advances in anti-aging therapy available through HGH (human growth hormone) peptides or other hormonally based therapies, we can help you on your journey toward wellness. Contact us today to get all your questions about peptides answered and to learn how this revolutionary type of therapy can make a true difference in your life.

